What is a Table in a Database?
A table in a database is like a spreadsheet. It organizes data into rows and columns. Each table holds information about a specific topic or entity, such as customers, products, or orders.
Think of a table as a container for structured data.
What is a Column in a Table?
A column represents a specific attribute or field of the data stored in the table. Each column has:
- A name (like CustomerName)
- A data type (like Text, Date, or Integer)
- A purpose (it stores the same type of information for all rows)
For example, in a Customers table:
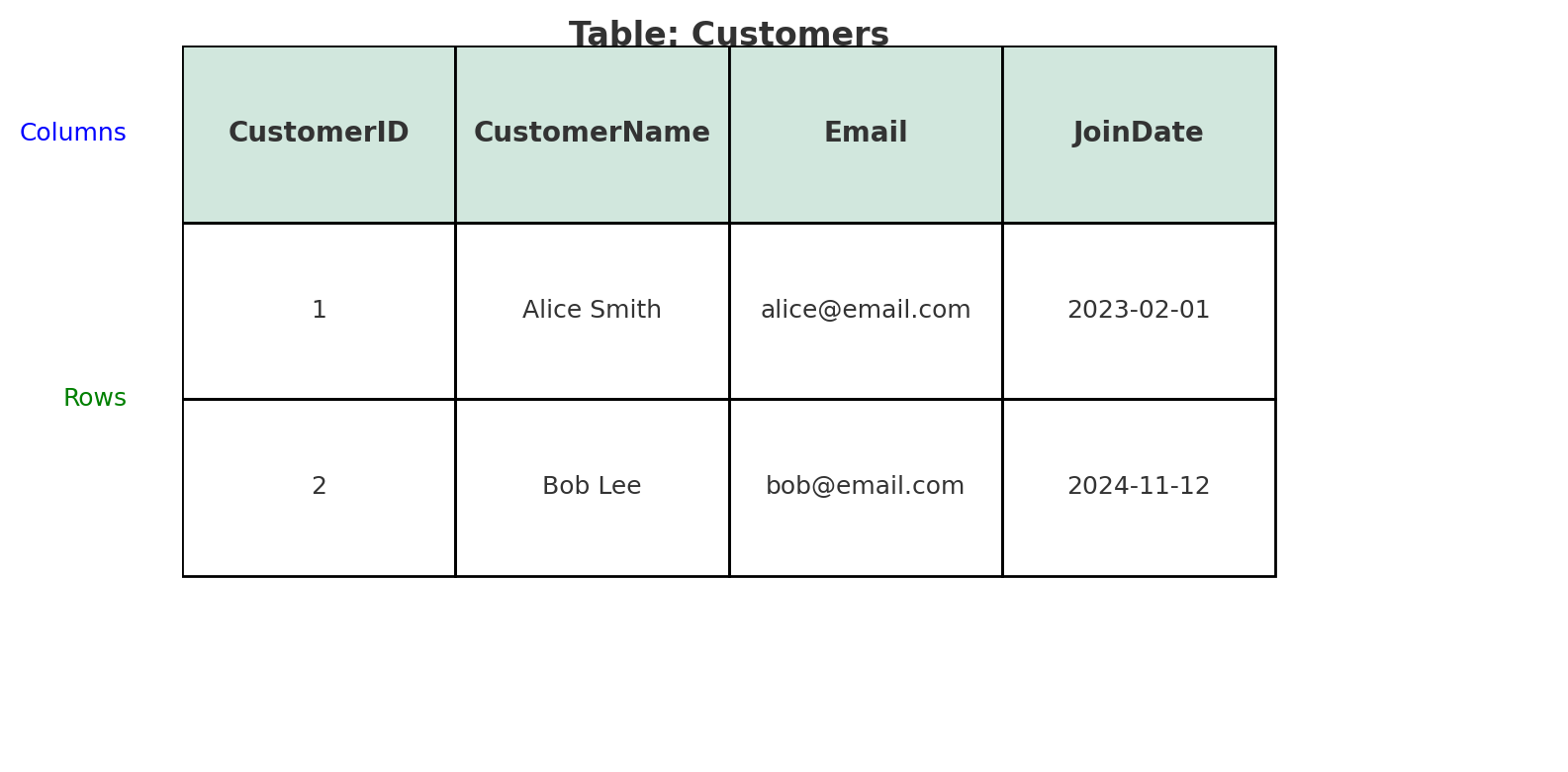
- Each row = a single customer (record)
- Each column = one attribute of that customer
Why Tables and Columns Matter
- Organization: Keeps data structured and easy to query
- Relationships: You can connect different tables (e.g., Orders table linked to Customers by CustomerID)
- Efficiency: Columns allow databases to index and retrieve data faster
- Clarity: Makes data easy to understand and analyze
Quick Analogy
Imagine a table as a class register:
- Each row is a student
- Each column is a student detail (name, age, grade, etc.)

Leave a Reply